Introduction
Cyber liability insurance costs are on the rise, and it's getting expensive. As companies deal with more cyber breaches, the price of protecting digital assets keeps climbing. Let's look at why this is happening and what it means for businesses trying to manage their cyber risk.
The Data Behind the Costs
When a company with cyber insurance gets breached, a whole process kicks into gear. Claim analysts review policies, incident response teams get called in, digital forensics experts investigate, and breach coaches help navigate the situation. All of this generates a ton of data.
NetDiligence compiles this data into annual reports, and that information becomes the foundation for how insurance companies set their premiums. The more expensive breaches become, the more insurance companies charge to cover that risk.
The Numbers Tell the Story
The stats are pretty eye-opening. Over five years, the average cost of a cyber incident for small to medium businesses doubled from $87,000 in 2018 to $169,000 in 2022. NetDiligence found over 254 claims from SMEs that exceeded $1 million each.
Here's what really stands out: 98% of these million-dollar claims came from companies making less than $2 billion in annual revenue. That's $1.6 billion in total claims from smaller businesses. These numbers show why companies of all sizes need to take cybersecurity seriously.
It's Not Just About Company Size
You might think bigger companies would have bigger losses, and you'd be right. But smaller companies actually face a bigger hit relative to their size. When a small business gets breached, the impact can be devastating.
Looking at the data, there's no clear connection between how many records get exposed and the total cost of an incident. What really drives costs up? Business interruption and recovery expenses. Over the past five years, business interruption costs jumped by 1,000%, and recovery costs increased by almost 300%.
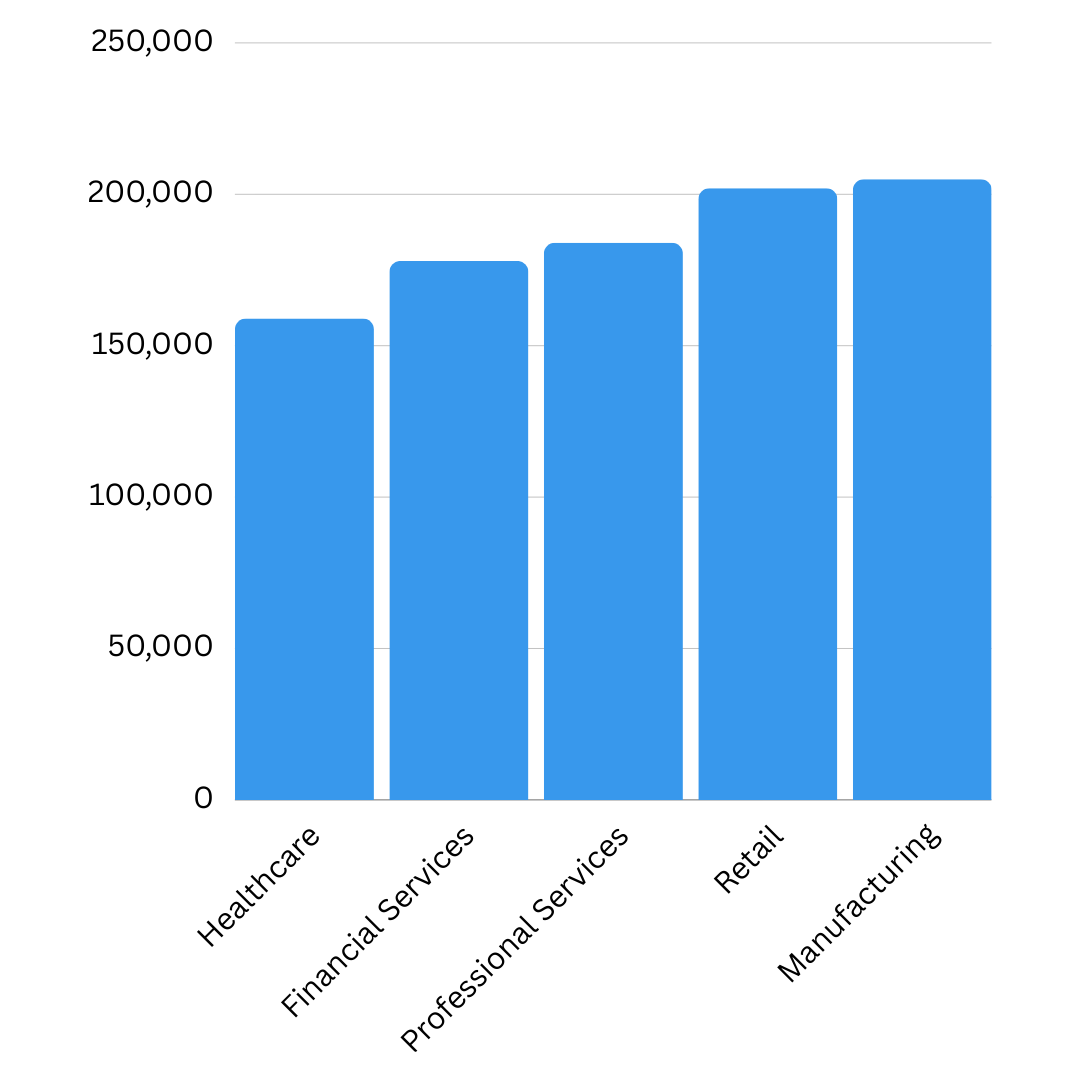
Interestingly, retail and manufacturing companies see the highest incident costs. That might surprise you if you expected heavily regulated industries like healthcare or finance to top the list.
The Main Threats: Ransomware and Email Fraud
When you look at what's actually causing these claims, ransomware and Business Email Compromise (often tied to wire fraud) account for about half of everything. Understanding these threats helps companies focus their security efforts where it matters most.
What Cyber Insurance Actually Covers
Cyber insurance can help, but it's not a magic bullet. Coverage varies widely. Some policies use automated systems that need minimal information. Others require detailed underwriting where you have to prove you have good cybersecurity practices in place.
The average "Self Insurance Retention" (SIR) for small businesses has gone up by almost 400%. That's the amount you pay out of pocket before insurance kicks in. It's a significant upfront cost that companies need to budget for.
The Reality of Rising Costs
As insurance gets more expensive, companies are finding that coverage has limits. Some costs just can't be insured. Reputational damage, lost opportunities during a breach, and the long-term impact on customer trust are hard to put a price on.
The good news? Prevention is often cheaper than insurance. Employee security training and regular penetration testing can be more cost-effective than just hoping insurance will cover everything.
Conclusion
Cyber liability insurance costs are going up, and that's not changing anytime soon. Companies need to understand what drives these costs, how different industries are affected, and what threats they're actually facing.
The best approach combines good cybersecurity practices with smart insurance decisions. By staying proactive about security, companies can reduce their risk and potentially lower their insurance costs. In the end, building strong cybersecurity defenses is still the best investment you can make.